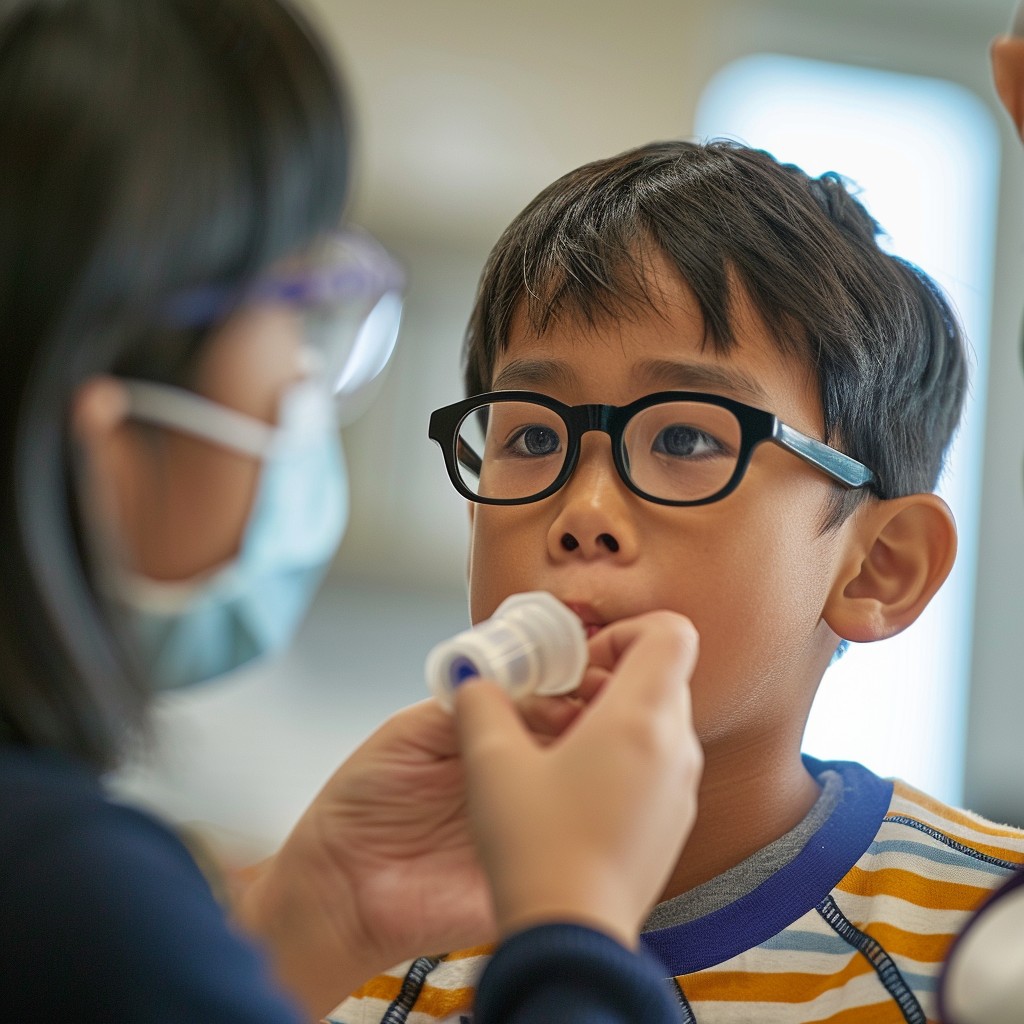
Have you ever stopped to think about the unsung heroes of the healthcare system? The ones who work tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure that patients with breathing disorders receive the life-saving care they need? Look no further than the world of respiratory therapy. Respiratory therapists are the backbone of the healthcare system. Working hand in hand with doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals to assess, treat, and manage patients with respiratory conditions. From premature infants struggling to take their first breaths to elderly adults battling chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, respiratory therapists are there every step of the way, providing expert care and support.
What is a Respiratory Therapist?
A respiratory therapist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of breathing disorders. They work with patients who have conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and cystic fibrosis, among others. Respiratory therapists use a range of techniques, including oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and medication administration, to help patients breathe more easily and improve their overall health.
Responsibilities of a Respiratory Therapist
The responsibilities of a respiratory therapist are diverse and challenging. Some of the key tasks include:
- Assessing Patients: Respiratory therapists assess patients’ respiratory status, including their breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and lung function.
- Developing Treatment Plans: Based on their assessments, respiratory therapists develop individualized treatment plans to help patients manage their breathing disorders.
- Administering Oxygen Therapy: Respiratory therapists administer oxygen therapy to patients who require supplemental oxygen to breathe.
- Managing Mechanical Ventilation: Respiratory therapists manage mechanical ventilation systems, which provide life-sustaining support to patients who are unable to breathe on their own.
- Conducting Pulmonary Function Tests: Respiratory therapists conduct pulmonary function tests to diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions.
- Educating Patients and Families: Respiratory therapists educate patients and their families on how to manage their breathing disorders, including the use of medications, equipment, and lifestyle modifications.
Requirements to Become a Respiratory Therapist
To become a respiratory therapist, one must undergo extensive training and education. Most respiratory therapy programs require a minimum of an associate’s degree. Many professionals opting to pursue a bachelor’s or even a master’s degree to advance their career. In addition to completing coursework in anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology, aspiring respiratory therapists must also pass a national certification exam to become licensed to practice. one must meet the following requirements:
- Earn an Associate’s Degree: Respiratory therapists typically earn an associate’s degree in respiratory therapy from a community college or university.
- Complete a Respiratory Therapy Program: Respiratory therapy programs are accredited by the Commission on Accreditation for Respiratory Care (CoARC) and include both classroom and clinical training.
- Pass the Certification Exam: Respiratory therapists must pass the Certified Respiratory Therapist (CRT) exam. Administered by the National Board for Respiratory Care (NBRC).
- Obtain State Licensure: Some states require respiratory therapists to be licensed to practice.
- Maintain Certification: Respiratory therapists must complete continuing education requirements to maintain their certification.
Specializations in Respiratory Therapy
Respiratory therapists can specialize in various areas, including:
- Neonatal Respiratory Care: Respiratory therapists work with premature infants and newborns who require specialized respiratory care.
- Pediatric Respiratory Care: Respiratory therapists work with children who have respiratory conditions, such as asthma and cystic fibrosis.
- Adult Respiratory Care: Respiratory therapists work with adults who have respiratory conditions, such as COPD and pneumonia.
- Critical Care: Respiratory therapists work in intensive care units, managing life-sustaining equipment and providing critical care to patients.
Conclusion
So the next time you find yourself struggling to catch your breath. Take a moment to appreciate the dedicated professionals who work tirelessly to ensure that you can breathe easy. Respiratory therapists may not always be in the spotlight but their impact on the lives of patients with breathing disorders is truly immeasurable.